Diving into E-Signatures
Prepared by Deborah Abrahams
Digital transformation changes the way an organisation operates. This includes the document signing process, which has shifted towards the use of e-signature to ensure a quick and efficient signing process. An e-signature, also known as an electronic signature, is a quick and legal way for a person to indicate consent or approval on a digital document. But what are the advantages of e-signature, and are there any drawbacks? Do you want to discover more about e-signature? Learn more about the types, benefits, limitations, and more in this article!
Table of Contents
The implementation of digital transformation has made organisations reevaluate their day-to-day operations. For example, the process of document signing has traditionally been carried out in-person, but organisations are gradually shifting towards the use of e-signatures to ensure that the signing process is carried out quickly and efficiently. This article focuses on the types, benefits, limitations, and use cases of e-signatures. It will also touch on the differences between e-signatures and digital signatures and provide a discussion of the various e-signature options that are currently on the market. Finally, the article will highlight several case studies of organistions that have used e-signatures to their benefit.
An e-signature, or electronic signature, is a simple and legally-recognised way for an individual to indicate his or her consent or approval on a digital document, and it reveals the signer’s intent to sign the document. E-signatures typically take the form of name-based signatures, although sounds, symbols, and numbered codes have also been used in the past. The history of e-signatures dates back to the 1800s when they were used by bankers, courts, and government agencies to receive important documents through electrical telegraphs (which may be thought of as one of the earliest forms of such signatures). Today, they are used in a wide range of applications, such as to enhance the processes of document management and volunteer applications, facilitate the development of sponsorship contracts, and customise signatures by staff members based on an organisation’s unique form of branding.
Differences between E-signatures and Digital Signatures
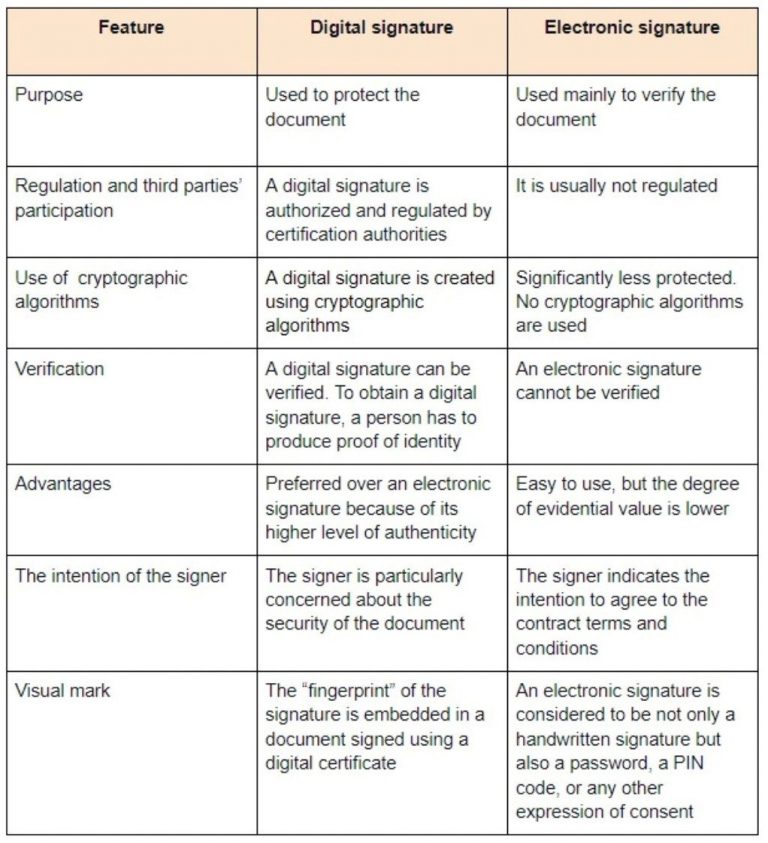
The terms “E-signatures” and “digital signatures” are often used interchangeably, as many think they mean the same thing. However, there are three key differences between them:
Function
E-signatures are used to verify or ensure that a document and its contents are accurate, and they are often associated with a contract that the signer agrees to. Digital signatures, on the other hand, are used primarily to protect a digital form or document from unauthorised access by other parties other than the owner of the digital document.
Method of Authentication
E-signatures require the signer’s email address, phone number, PIN code, etc. to authenticate their signatures. On the other hand, the ‘fingerprint’ of a digital signature is embedded within a document that is signed using a digital certificate, which is a file that verifies the identity of the user before granting them access to the document. This digital certificate is necessary for a digital signature because it provides the public key that is used to validate the private key that is associated with a digital signature. This process is known as Certificate-Based Authentication.
The table below provides some additional comparisons (including those mentioned above) between the two different types of signatures.
Types of E-Signatures
The Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services (eIDAS) is categorised e-signatures into three main levels: Simple electronic signatures, advanced electronic signatures, and qualified electronic signatures.
Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)
Simple Electronic Signatures (SESs) may be defined as ‘electronic data that is attached to or logically associated with other forms of electronic data which signers sign on’, which means that something as simple as writing a name under an e-mail would constitute an electronic signature. Simple Electronic signatures are the most used type of e-signature because they are easy and quick to use. They are used when individuals sign for parcels on a terminal, click on the “I Consent” button on a volunteer waiver form, or upload a picture of a signature to sign a registration form.

Level of Security
Although SESs are simple to use and don’t require any verification, it also makes it easy for people to deny having signed the document. Individuals may therefore take the following steps during the signing process to verify the signer’s identity:
- Send an SMS code to signers as a form of acknowledgement
- Require signers to key in their PINs
- Require signers to key in passwords that are sent to them
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AdES)
Advanced Electric Signatures (AdES) are relatively more secure than SES, which makes them more suitable for use in documents with legal significance and financial transactions. AdESs are used during:
- Agreements for grant sponsorships
- Large online business transactions
- Electronic fund transfers

Level of Security
The following additional requirements must be met by an e-signature for it to be considered as advanced:
- The signature must be uniquely linked to and capable of identifying the signer.
- The signature must be created in a way that allows the signer to retain control. This includes creating an authentication method that can only be used by the signer, such as the use of the signer’s personal mobile phone to perform the action.
- The signature must be linked to the document in a way that causes any subsequent changes to the data to be detectable. The signature will be invalidated if any changes to the accompanying data are discovered.
The most used technology that can provide these requirements relies on the use of a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). A PKI is the framework of internet encryption and cybersecurity used on web browsers to protect communications between a website and its users, and it involves the use of both certificates and cryptographic keys.
There are a few actions that individuals may take to meet the above requirements:
- Conduct a live verification and/or upload the signer’s ID
- Use an audit trail or a sequence record as evidence
- Make use of face-to-face verification, which may be done either physically or remotely
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
Qualified electronic signatures (QESs) provide the most advanced levels of security, but they can be difficult to implement and should therefore only be used in very specific cases. QES may be used in well-supervised legal transactions where it may be used as a substitute for a wet signature, namely during the signing of legal forms and documents with high liability risks.
In addition to the requirements for AdES, a QES must also be:
- Created by a qualified signature creation device (QSCD);
- Based on a qualified certificate for electronic signatures;
- Used in scenarios where they are essentially equivalent to a handwritten signature.

Level of Security
The procedures required for QESs are similar to those for AdES. The only difference is that the signer’s identity must be verified beforehand, and the signature key must be kept in a Qualified Electronic Signature Creation Device (QSCD). Identification of the signer’s identity is usually done physically, although it may be carried out remotely under specific requirements:
To use a QES. Signers must be given an identification token to help verify their identities. The tokens must be well-protected, reliable, and able to be used for up to 3 years. Examples of identification tokens include:
- Smart Cards
- USB Keys
- Badges
Benefits of Electronic Signatures

Easy-to-Use
E-signatures speed up the document signing process for both employees and beneficiaries. They are also easy to learn due to the intuitive nature of most electronic signature software systems.

Improves Document Accuracy
The e-signature field on an electronic document is often a mandatory one, which helps to reduce or even prevent the risk of missing information due to human error.

Helps save on Time and Money
The time and costs needed to manually send out and track the signing process can be reduced with the help of e-signatures, The amounts of time saved may instead be used more productively to build and improve relationships with beneficiaries and reach organisational goals.

Enhances Customer Service
E-signatures allow organisations and their clients to sign important documents conveniently from anywhere, at any time, and on any device, which can be appealing to signers, especially those from younger demographics.
Limitations of E-Signatures

Limited Storage Options
Some e-signature vendors may require their users to store documents and data on their servers, which could prevent users from having control over sensitive information. The control of data should typically be transferred over to users, and copies of documents should be removed from e-signature servers.

Some Software is Propriety
Organisations that make use of closed-source software may find themselves locked into a single e-signature vendor, which can be troublesome if they would like to switch vendors in the future. This can be avoided by choosing flexible vendors and suppliers which will allow these organisations to switch between vendors easily.
Best Practices of E-Signatures
It is important for organisations to make use of e-signatures in a suitable manner to ensure that the signing process between organisations and beneficiaries takes place smoothly. Here are some good practices to follow when using e-signatures:
Give Signers Access to the Right Documents
Ensure that the correct documents are successfully delivered to the intended recipients, and that they are able to access the sent documents.
Authenticate Signers
Authenticate the signer’s identity through the use of PINs or One-Time Passwords (OTPs). Authentication methods may vary depending on whether the recipients are new or existing beneficiaries.
Review Document Presentations
Decide how documents will be presented to their intended recipients beforehand before sending them for signing. We recommend that these documents be sent through a web browser so that additional pieces of software do not need to be downloaded.
Get the Recipient’s Data at the Time of Signing
Data fields should be added to a document to allow organisations to retrieve additional data from signers during the signing process.
Allow for the Attachment of Additional Documents
Allow for the attaching of additional documents to assist in authenticating the information provided and to speed up the signing process.
Ask for Consent during the Signing
Ensure that the recipient consents to the signing process by prompting them to press a “click to sign” button and/or provide a digitised handwritten or smartcard signature.
Deliver the Signed Document to all Parties
A signed copy of the document should be sent securely to the signer or signers to allow them to print the signed documents.
E-Signature Options on the Market
The wide range of e-signature options currently available on the market can often make the selection process difficult for organisations as certain e-signature platforms will suit their needs and budgets better than others. Here are some popular e-signature options along with their key features to help potential users select the right e-signature vendor for their needs.
HelloSign
The HelloSign platform allows its users to choose from a range of e-signature types for different types of documents, including new employee agreements, NDAs, and loans. First-time users have access to a free trial for them to test out the platform’s customisable features and explore its ready-made templates before deciding whether to purchase any of their three packages. HelloSign is also available on mobile devices and desktops and includes APIs that enable third-party integrations.
Adobe Sign
Adobe Sign allows documents to be signed more quickly and offers advanced features such as template creation and real-time notifications for its team members. It also allows for documents to be sent in bulk. Organisations also have access to its Mega Sign feature, which allows for the document template to be sent to multiple recipients at once and for each document to be signed separately. Adobe Sign’s intuitive API allows it to be integrated with third-party apps such as Microsoft Office 365, and it is available on both desktop and mobile devices.
DocuSign
DocuSign offers its users features such as standard or customised tags and fields as well as the ability to convert documents into PDF formats. The platform also allows for documents to be retrieved from cloud storage services. DocuSign allows users to specify the intended number of signers for each of their documents and to administrator control over user roles and permissions. The platform also requires signers to pass through multiple layers of verification using emails, access codes, and federated identities to ensure the safety of the signing process.
PandaDoc
Organisations who would like the flexibility to customise their forms and e-signatures may choose to use PandaDoc, a platform that simplifies the editing, signing and creation of documents. It also features notifications, collaboration insights, and helpful tips on how to improve the signing process. PandaDoc may be integrated with various pieces of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software such as Hubspot and Salesforce and it comes with a wide array of templates for contracts, forms, quotes, and so on.
Signaturely
Signaturely’s intuitive design and user-friendly interface allows organisations to host documents securely on their websites. These documents may either be kept private or stored digitally on a password-protected page, which allows them to be easily accessed and managed. The platform also offers its users ready-made templates and automatic notifications to facilitate and enhance the signing process.
E-Signature Use Cases
Document Management
Organisations or individuals may use e-signatures to upload, send, and sign documents much more quickly, and be notified during each step of the process.
Volunteer Applications
E-signatures are particularly helpful when they are used in volunteer agreement forms and check-in/check-out forms as it allows signatures to be collected much more efficiently.
Membership Renewals
E-signature platforms allow organisations to efficiently renew their teams’ and stakeholders’ memberships by sending forms electronically in bulk. Organisations may also use various payment tools to collect membership fees and share information with both their new and current members.
Fundraising Registration Forms
Donors may send their signatures quickly and digitally through the use of e-signatures. E-signature platforms may also be used by organisations to track the progress of their fundraising programs and obtain insightful analytics.
Customise and Bulk-Send Forms
As mentioned earlier, e-signature requests may be sent in bulk with a single click. These signature requests may also be customised to fit an organisation’s brand.
Facilitate Expense Reporting
Employees and volunteers can create and sign expense reports electronically to help with the reimbursement processes, which is also helpful for keeping all company receipts in a single, centralised location.
Sponsorship Contracts
Organisations may sometimes create sponsorship request forms with customisable details such as the intended use for funds, purpose of use, and termination dates in the contract. Both parties may make use of e-signatures to sign these contracts quickly and save them in a secure place.
How to Use E-Signature Platforms
TQ has written a white paper on e-signatures that non-profits and other organisations may use as a tutorial on how to make use of these types of signatures. The white paper provides a step-by-step guide to making a general signature request on HelloSign’s Membership Registration and Volunteer Waiver Forms. It also provides other tutorials on each of the e-signature platforms listed above (HelloSign, Adobe Sign, DocuSign, PandaDoc, and Signaturely).
Case Studies
1
One Tree Planted, a non-profit organisation focused on reforestation, found their typical pen-and-paper-based document-signing processes to be wasteful (both in terms of time and resources) and challenging to track. Additionally, face-to-face signings became increasingly difficult to carry out during the COVID-19 pandemic. Using PandaDoc’s templates allowed the non-profit to efficiently track and sign agreement forms and NDAs, which allowed the organisation to save time that was previously spent chasing individuals for signatures. Implementing e-signatures also helped One Tree Planted fulfil their organisational mission or North Star of being more environmentally conscious.
2
Grayson College was faced with large amounts of paperwork due to the high volume of student intakes each year. The college therefore used HelloSign to digitalise 100 out of 239 of their common form types (most of which were financial aid forms and work-study applications), which allowed their students to conveniently fill up those forms from their online dashboards.
3
Cats Protection, the UK’s largest feline charity, was on their road of digital transformation. After introducing cloud-based collaborative platforms such as Microsoft Teams, the non-profit looked at digitalising its adoption forms, which were previously generated and distributed by hand (a tedious and time-consuming process). Using Adobe Sign allowed Cats Protection to send documents to pet owners for signing and store all their adoption documents online to make them readily accessible to employees, volunteers, and pet owners. By implementing e-signatures, the organisation was able to drastically reduce the processing time for adoption from 2 weeks to just 2.5 hours.9
Summary
- An e-signature is a tool that is used to confirm a person’s intention to sign a document.
- E-signatures and digital signatures differ in several ways, but mainly in terms of their functions and methods of authentication.
- The three main types of e-signatures are, in increasing levels of security, Simple Electronic Signatures, Advanced Electronic Signatures, and Qualified Electronic Signatures.
- Benefits of e-signatures include being user-friendly as well as the ability to save on time and money, improve document accuracy, and enhance customer service.
- Some limitations of e-signatures include limited storage spaces or options and software propriety.
- Some good practices in e-signatures include giving signers access to the right documents, authenticating signers, reviewing document presentations, retrieving recipient data, attaching additional documents, asking for recipients’ consent, and sending signed documents to all parties involved.
- Some popular e-signature platforms include HelloSign, Adobe Sign, DocuSign, PandaDoc, and Signaturely.
- Organisations can use e-signatures to enhance document management, automate volunteer applications, develop sponsorship contracts, customise signatures based on an organisation’s branding, facilitate expense reporting, and renew memberships.
- Case studies from One Tree Planted, Grayson College, and Cats Protection show that implementing e-signatures can lead to the automation of manual, paper-based processes as well as efficient and environmentally safe signing procedures.
